Arthritis is a degenerative disease that affects the normal functioning of one or more joints. Arthritis causes damage to a critical tissue covering the joints, which leads to joint swelling and tenderness.
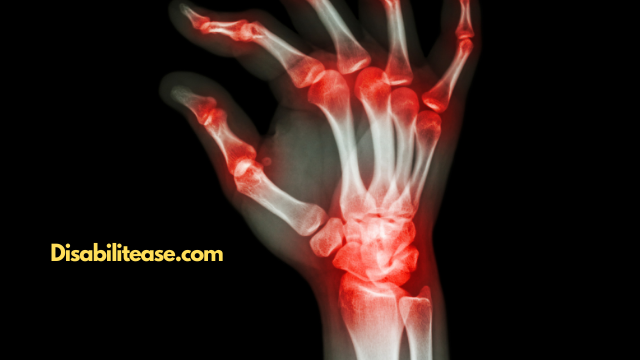
Most cases of Osteoarthritis are non-erosive. It refers to the typical case of Osteoarthritis that only brings mild damage and thinning of the protective tissue.
It is called non-erosive because of its benign nature, where it doesn’t completely erode the joint lining.
Before we can understand non-erosive Arthritis, it’s important to understand the overall complications that Arthritis causes.
Here is a related article that might interest you on Best Handguns for Seniors and Arthritis Patients for Home & Self-Defense.
Some prevalent types of the disease include Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. The two subtypes affect the body differently and therefore need different care.
Table of Contents
What Is Non-Erosive Arthritis?
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis affects nearly 33 million people in US and more than 500 million people globally. Every human joint has a protective lining made up of hard but slippery tissue that acts as a cushion against the different bones that scrub together.
Osteoarthritis causes damage to this protective layer, called the cartilage, and causes more friction during joint-related movement. The friction can start a ripple effect where the lining gets more damaged and causes pain as the joints are engaged during day-to-day activities.
In severe cases, this lining can become severely deteriorated and cause direct contact between the two bones forming a joint. The most commonly affected joints include the spine, hips, knees, and hands.
While no permanent treatments are currently present, it is a highly manageable disease. It’s important to follow some preventative rules because it can progress into a more serious condition and cause bone erosion.
One of the most common measures is staying active and maintaining a healthy weight. There is also medication that can help slow down the progression, but the damage cannot be reversed through surgery or implants.
The condition usually progresses very slowly, with most cases reporting only minor growth in 5 or more years. However, it can worsen quickly due to poor habits, diet, lifestyle choices, and weight gain.
Non-Erosive Osteoarthritis
Most cases of Osteoarthritis are non-erosive. It refers to the typical case of Osteoarthritis that only brings mild damage and thinning of the protective tissue. It is called non-erosive because of its benign nature, where it doesn’t completely erode the joint lining. More than 98 percent of Osteoarthritis cases are non-erosive and can be managed easily. Even though the disease can progress into a more serious condition, total depletion is still rare.
Non-erosive Osteoarthritis is not classified as “non-erosive” due to any unique complications but indicates the absence of Erosive Arthritis Only.
Erosive Arthritis, on the other hand, is a highly rare condition and accompanies total depletion of cartilage.
Erosive Arthritis usually affects middle-aged women and attacks the smaller joints within the fingers or hands.
Treatments For Osteoarthritis
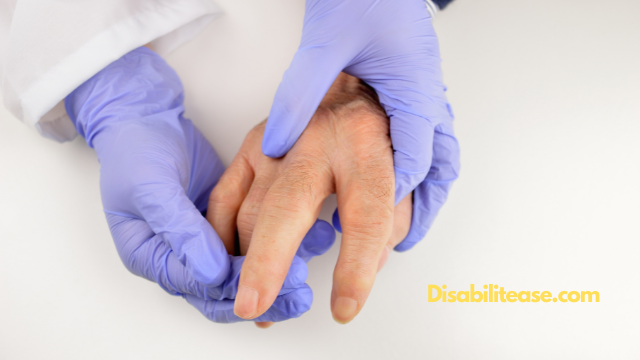
Most treatments for Osteoarthritis are designed for symptom management and deceleration of progress. Common treatments include oral or topical pain relievers, corticosteroids, and NSAIDs.
The type of treatment that works best for your case can vary based on the severity and the specific joint affected.
Oral Pain Relievers are a great choice for increased pain but don’t work very well against swelling. NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are an all-rounder solution when your condition has multiple severe symptoms, including pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
While also a chronic inflammatory disorder, Rheumatoid Arthritis is more commonly classified as an autoimmune disorder due to its direct relation to the immune system.
The condition causes damage to the joint tissues, and blood vessels and leads to severe inflammation. Under Rheumatoid Arthritis, the immune system mistakes the essential joint tissues as a threat and causes all the complications.
It is believed to be more severe than Osteoarthritis due to multiple reasons. Firstly, it can progress more quickly and impact your heart, lungs, and eyes. Secondly, it can cause serious physical disabilities due to bone erosion and joint deformity.
Another important symptom that makes it more serious is the joints it affects. While Osteoarthritis is more common in the bigger joints like the hips and knees, Rheumatoid Arthritis affects joints within the fingers, hands, and feet. This can make everyday tasks a bigger challenge. The condition can lead to joint deformity and displacement when not managed properly.
Non-Erosive Rheumatoid Arthritis
Compared to Osteoarthritis, where most cases are non-erosive, more than 98 percent of Rheumatoid Arthritis cases are erosive. This makes Rheumatoid Arthritis more serious and uncontrollable than the other subtypes.
Over time, the friction from the unprotected joints can cause complete depletion of the protective layer making the bones grind together every time the joint is engaged.
Common Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
The condition is currently untreatable and irreversible. The aim of most medications and treatments is to slow down the disease’s progress and relieve pain.
Moreover, its detection can be difficult due to the inconsistent symptoms. Most of the symptoms, including swelling, pain, and burning sensations, usually come in sudden flares and then cease for a period.
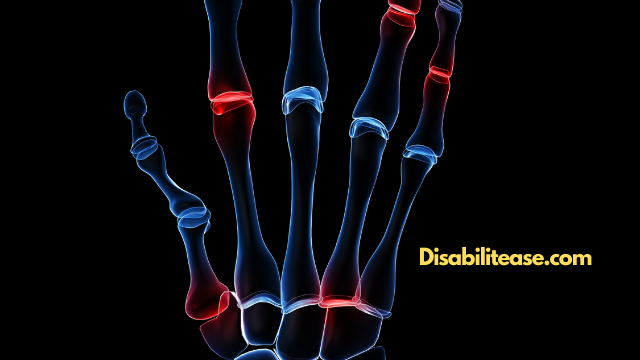
Rheumatoid Arthritis is usually treated with disease-modifying drugs (DMARDs) and Biological treatment. However, the initial treatment after diagnosis includes a trial of different DMARDs only. DMARDs are anti-rheumatic drugs that block the adverse effects of your immune system attacking the joints.
By preventing the released chemicals from reacting within the joints, they prevent damage to the surrounding tendons, cartilage, and ligaments.
Some of the popular choices include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and leflunomide. Different types of DMARDs will have different levels of efficacy for each patient. For this reason, Your GP will typically prescribe different types of DMARDs until the one with the best results is found. The treatment can also be accompanied by topical steroids such as corticosteroids to help relieve pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Signs and Symptoms of Non-erosive Arthritis
Low Flexibility
Most patients struggle to achieve a fuller range of movement within the affected joint. This symptom is more commonly evident during the first few hours after waking up and subsides with a more active lifestyle.
Tenderness
The affected joint feels tender to touch and often becomes more painful as the day progresses. Its occurrence can vary with each patient, where some experience it during activity while some after the activity.
Grating Sensation
Affected joints can often make a cracking sound as you engage them, especially within a wider range of motion. This usually happens due to the thinning protective layer and the fluid within it; the increased friction between your bones causes the grating sounds.
Swelling
The inflammation of soft tissue surrounding an affected joint can cause mild to severe swelling flares. Due to this, the joints also appear to be larger and rounder than usual.
Stiffness
This is more common when waking up and happens due to long periods of inactivity.
Another post that will interest you is about What Are Arthritis Blood Tests?
Conclusion
There are many different types of arthritis. And we are happy that now you have an understanding between other types and non erosive arthritis.

Hi, my name is Eddie, I am a professional trainer specializing in the elderly population and I’m also a website designer. I love training in the gym, going to the beach, traveling, and having good food.
I combined my love for sport and website designing to make “DisabilitEase” whose purpose is to help elderly and disabled people live a more full and active life, have more fun, and enjoy their unique journey despite any disability.




